Increase of production of cement can be achieved by of extraction of natural resources and construction of new plants for processing these natural resources. However, this is a costly and environmentally detrimental method.
At the same time, waste of ferrous metallurgy contain an enormous amount of oxidised steel slags with a high basicity.
After meltdown of such slags in the smelting unit MAGMA and partial reduction by carbon of oxides contained in them by process route shown below, we get molten slag (molten clinker) similar by its chemical composition to cement clinker manufactured by conventional methods at existing cement plants (Table 1).
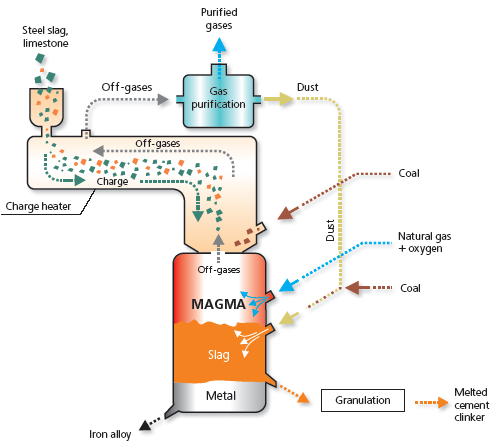
Table 1. Chemical composition of oxidised steel slag, cement clinker and Portland cement type СЕМ 1
| Material | Content, % | |||||||
| CaO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | MgO | Fe2O3 | MnO | Fe, корольки | SO3 | |
| Oxidised steel slag | 40-45 | 1,5-3 | 15-19 | 1,5-2,5 | 18-25 | 4-7 | 4-6 | -- |
| Slag smelted and partially reduced in MAGMA |
61,7-63 | 1,8-3,7 | 18-24 | 1,8-3,1 | 4,5-5,2 | 2,5-4 | 0 | -- |
| Conventional cement clinker | 60-67 | 3-8 | 17-25 | 2,5-5 | 4-5 | -- | 0 | -- |
| Typical Portland cement type СЕМ 1 | 62-64 | 5,5 | 21,5 | 1,5 | 3-4 | -- | 0 | 1,9 |
Production capacity of MAGMA for clinker is 200,000-250,000 tpy and depends on chemical composition of the slag being processed and energy carrier used.
Up to 800 kg of melted cement clinker and up 250 kg of iron alloy can be produced out of 1 ton of re-smelted steel slag.
This allows to significantly reduce the costs of production of the melted clinker.
Production of melted cement clinker out of ferrous metallurgy waste allows to decrease the environmental impact due to refusal from the use of natural resources, reduce energy intensity of production and CO2 emissions per ton of products, i.e. achieve a significant environmental improvement (Table 2).
Table 2. Comparative figures of cement clinker production methods
| Production method | Raw materials | Saleable products |
Energy carriers used |
Specific units per 1 ton of product | ||||
| Limestone consumption |
Natural gas consumption |
Coal consumption |
Off-gases volume |
CO2 emissions |
||||
| kg | m3 | kg | kg | kg | ||||
| Conventional method | natural resources (clay, limestone) |
cement clinker |
natural gas, electric power |
1 150-1 850 | 82-96 | - | 1 500-1 700 | 720-840 |
| MAGMA method |
ferrous |
cement clinker, iron alloy |
natural gas, electric power, coal |
50-570 | 60-70 | 70-110 | 520-930 | 290-615 |
